
Ten Days Online FDP on Advanced Remote Sensing and Machine Learning for
Environmental Sustainability
Session X : MOSDAC Data and hands on training for ocean color data - Dr Shivani, Scientist SG, Space Application Centre – ISRO, Government of India.
Highlights of the Session - X
-
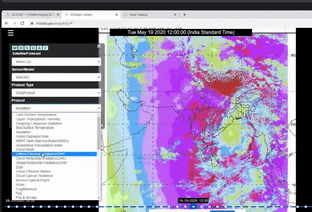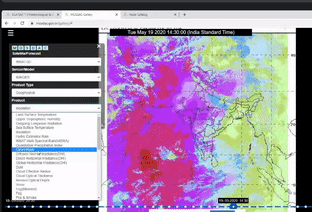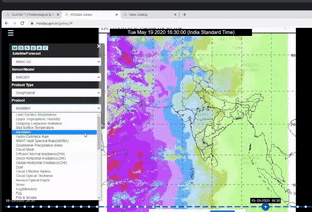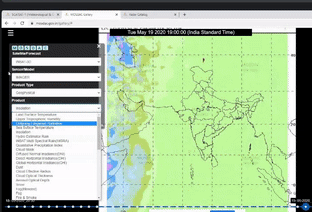
A clear-cut demonstration of the usage of MOSDAC(Meterorological and Oceanographic Satellite Data Archival Centre) Web Geo Portal (URL: mosdac.gov.in) was done. The website provides realtime data products to the users.
-
The demonstration of all the main functionalities available on the site was given.
-
Firstly, the mission gallery was accessed and information about eight different satellites – Scatsat-1, INSAT 3DR, INSAT 3D, Kalpana-1, INSAT-3A, Mega Tropiques, SARAL Altika, Oceansat-2 was presented.
-
Various applications such as Safe Beach, city weather forecasting, Heat waves, cold waves, heavy rain forecast, monsoon, solar & wind, sea state, cloud burst, cyclone, soil moisture, Vayu, Varsha, Urja was detailed.
-
MOSDAC live application comprising quick layers, tools, animations, analysis and legends was explained.
-
And, finally downloading of satellite data and user registration in the portal was demonstrated .
Session XI : Google Engine and Deep Learning algorithms - Dr. Prasun Kumar Gupta , Scientist SE, Indian Institute of Remote Sensing - ISRO, Government of India.

Highlights of the Session - XI
-
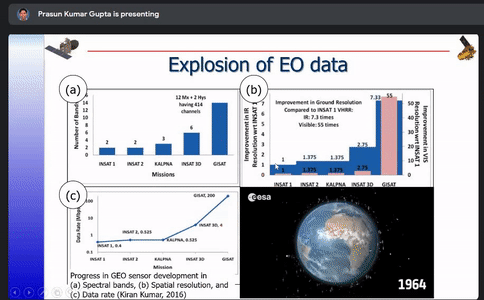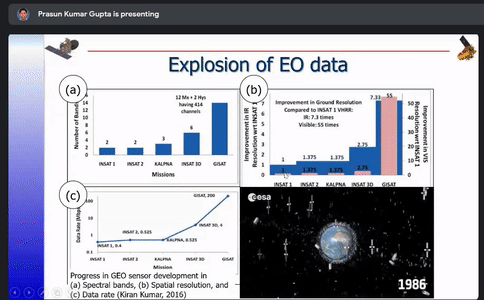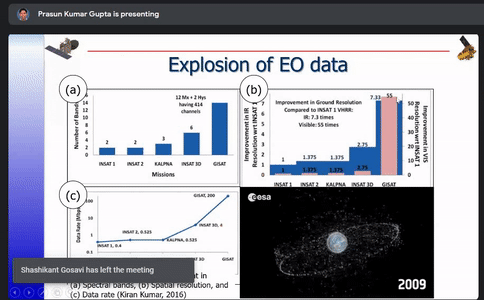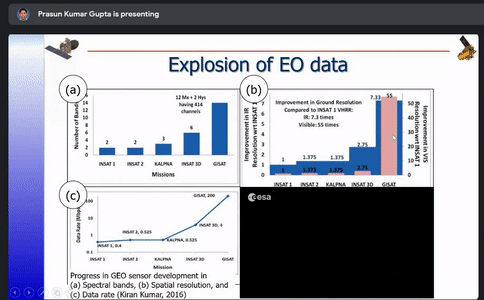
Various Indian Earth Observation programs such as EOS-6, NISAR, INSAT-3 DS,RESOURCESAT-3 and 3A and their applications were listed out and basics of cloud computing along with the differences between traditional and cloud computing were discussed.
-
Open source cloud technologies involving framework, query/data flow, data access and data base; orchestration and MGMT; streaming and messaging were described.
-
The list of GIS cloud technologies such as ESRI cloud services, Microsoft Planetary Computer, Google Earth Engine, MAPBOX, QGISCLOUD, AMAZON OPEN DATA, etc.., were showcased.
-
Earth Engine Public Data Catalog which uses Landsat, Sentinel, MODIS, terrain and land cover data was narrated. The concept of time lapse and other studies of forest loss in Assam 1984-2016), development of greater Noida (1990- 2016), Shrinking of Bellandur lake (1984- 2016), construction of Theri dam (1991-2010) were also explained.
-
Google Earth Engine and its application such as land cover classification on GEE, Sea grass mapping on GEE were described. Advantages of GEE like high speed processing, offering wide range of geospatial processing, access to already processed datasets and debug etc.., were pointed out.
-
Surface water spread analysis using Landsat, MODIS, Sentinel data was explained with the case study done on parts of Ghaghara river, India. Water spread from time series satellite data,geomorphology applications were also explained.
-
Topics like Global surface water explorer, surface water charges (1985- 2016), climate engine, Map of Life (MOL) were given an insight.
-
The data types used in GEE and its various geospatial processing functions like image, image collection, feature, filter, reducer, kernel, projection were described.
-
The steps like getting an image, applying an algorithm to the image, filtering a collection, mapping an algorithm over a collection, reducing the collection and computing aggregate statistics were narrated.
-
Different types of deep learning algorithms like classification, regression, clustering and dimensionality reduction were explained and the open source software landscapes like Tensor flow, transformers, WEKA, Keras, BERT, Caffe, VELES, Spacy, neon, Aeroslove, etc. were showcased.
-
The major differences between artificial intelligence, machine learning and deep learning were explained and genesis of deep learning algorithms, Feed Forward Neural Networks and Perceptrons were discussed.
-
The various types deep feed forward (DFF), Recurrent Neural Network (RNN), Long Short Term Memory (LSTM),Auto Encoder (AE), Deep Convolution Network (DCN), Generative Adversarial Network (GAN) were discussed.
-
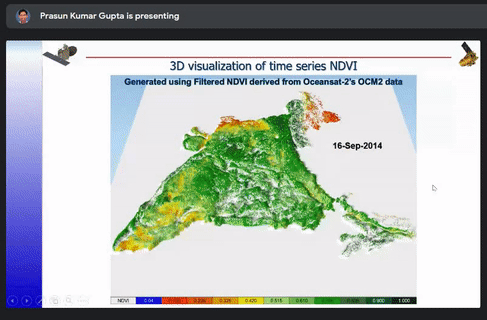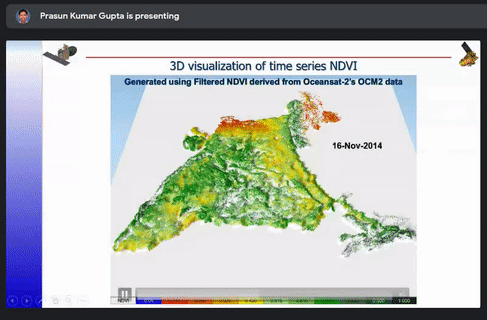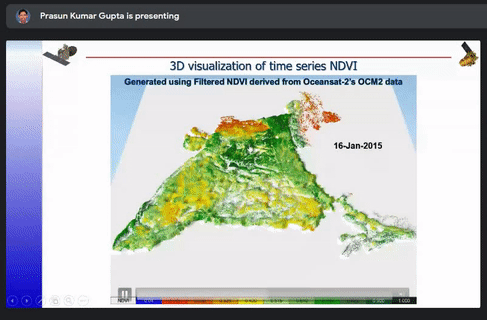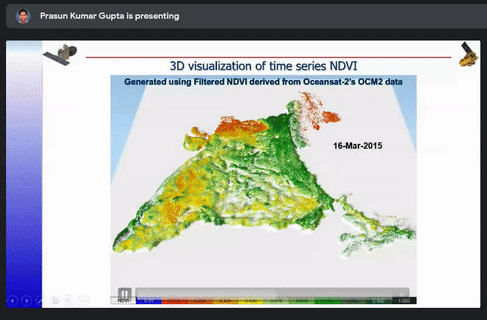
The different ways to optimize a model such as Architectural and Hyper parameter were also briefly explained. The case studies of snow and cloud discrimination, crop mapping, 3D visualization of time series NDVI, inter-calibration of night time satellite data and GAN based coal fire mapping were explained.